What is an atmosphere?
The Earth’s atmosphere is a layering of gases that surround the globe. Without the atmosphere, life on Earth would not have been able to form or evolve. It provides protection against the vacuum of space and the harmful rays of the sun.
People who study the atmosphere are called atmospheric scientists, or aerologists. Atmospheric scientists and meteorologists (weather scientists) can study the weather by sending data collection devices, like a “weather balloon,” into the stratosphere, a layer of the atmosphere.
What purpose does the atmosphere serve?
The protection that the atmosphere provides comes from its insulating abilities. This means that it absorbs much of the heat that radiates off of the sun, while simultaneously preventing the escape of heat that comes from the Earth—much like how the insulation works in a house.
This insulation is meant to keep the Earth’s temperatures relatively stable, and especially to keep some warmth in place even when night falls. An additional portion of the atmosphere is the ozone layer, which helps reduce the amount of radiation that the Earth receives from the sun.
Another primary thing the atmosphere regulates is Earth’s climate and weather patterns. These patterns of weather help prevent a buildup of too much heat in one location, a process that leads to rain and storms. These tasks are important to the survival of life on Earth.
Due to the Earth’s gravitational force, other functions of the atmosphere include creating pressure within the surface of the Earth, which makes liquid states, like water, possible.
What is in the atmosphere?
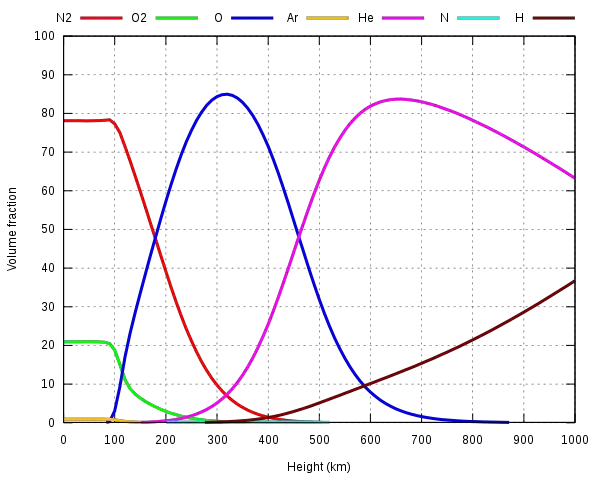
The primary elements that make up the Earth’s atmosphere are nitrogen and oxygen. There are many other elements that help make up the atmosphere as well, such as carbon dioxide, which is necessary for plant survival and photosynthesis.
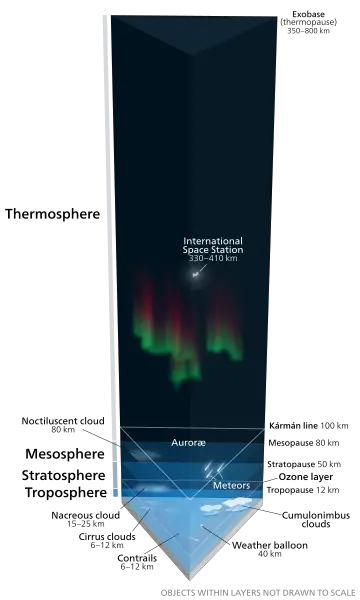
What are the layers of the atmosphere?
There are also five separate layers of atmosphere. The outermost layer is called the exosphere, and it’s the thinnest. It reaches as high as 10,000 kilometers above the surface of the Earth. The next layer in is the thermosphere, which can get very hot.
The next layer down from the thermosphere is the mesosphere, which goes on for about 50 miles. After that is the stratosphere, which goes on for about 30 miles. Finally, the layer closest to the surface of the Earth is the troposphere, which goes up to as high as 50,000 feet.
Weather patterns occur in the troposphere. And even though airplanes fly very high at 30,000 feet, they still fly within the first layer.
Damage to the atmosphere
Any life, plant or animal, would not be able to exist on Earth without the atmosphere as it is. The oxygen is what keeps us breathing, and the insulating properties keep us at livable temperatures. But for the past hundred years, the atmosphere has been receiving damage from air pollution.
These damages to the atmosphere are what lead to increasing global temperatures, holes in the ozone layer/increased risk of radiation from the sun, and even acid rain in some areas.
Questions:
- What is an atmosphere?
- What does the atmosphere do?
- What does the ozone layer do?
- What are the primary elements that make up the Earth’s atmosphere?
- What are the layers of the atmosphere?

Answers:
- The Earth’s atmosphere is a layering of gases that surround the globe.
- The atmosphere provides protection against the vacuum of space and the harmful rays of the sun.
- The ozone layer helps reduce the amount of radiation that the Earth receives from the sun.
- The primary elements that make up the Earth’s atmosphere are nitrogen and oxygen.
- The atmosphere is made up of the exosphere, thermosphere, mesosphere, stratosphere, and troposphere.