From their snow tipped peaks to their forest filled bases, mountains are certainly impressive. Some people like to look at them, while others enjoy climbing to their very tops.
Most geologists require a mountain to be at least 1,000 feet above the surrounding area. When several mountains are close to each other, it is called a mountain range.
Geologists separate mountains into five groups: fold, fault-break, dome, volcanic, and plateau.

Fold Mountains
The most common type of mountain is a fold mountain.
Fold mountains are created when two tectonic plates converge or collide with each other. This results in miles and miles of the Earth’s crust rising into a mountain range.
The Rocky Mountains in North America, the Alps in Europe, and the Himalayan Mountains in Asia are all examples of fold mountains.
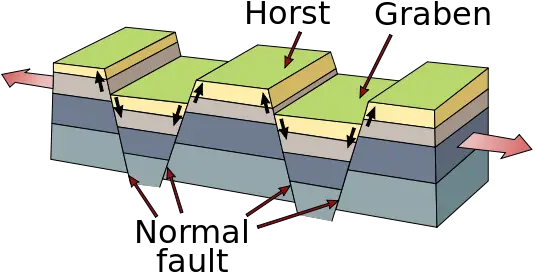
Fault-Block Mountains
Fault-block mountains are also simply called block mountains. They are created by faults. Faults occur where tectonic plates rub up against each other, but don’t collide head on.
The faults break up the rock, forcing some of the blocks up and some down. The blocks that are pushed up are called horsts, and the blocks that are pushed down are called graben.
Fault-break mountains usually have sharp, cliff like fronts and sloping backs.
The Sierra Nevada Mountains in North America and the Harz Mountains in Germany are examples of fault-block mountains.
Dome Mountains
Another name for dome mountains is upwarped mountains. They get this name because dome mountains are created when magma is pushed up towards the Earth’s crust. The magma is never erupted, but causes the crust to rise, forming a dome mountain.
Dome mountains get their classic dome shape from erosion and weathering.
Half-dome in Yosemite National Park and the Black Hills of South Dakota are examples of dome mountains.
Volcanic Mountains
You will not be surprised to find out that volcanic mountains are created by volcanoes. Volcanoes erupt hot magma in the form of lava, and ash from beneath the Earth’s crust. The magma cools upon itself and creates the mountain.
Volcanic mountains are continually being built upon so long as the volcano is active.
Some of the largest mountains in the world are volcanic mountains.
Some examples of volcanic mountains are Mauna Kea in Hawaii, Mt. Rainier in Washington, and Mt. Fuji in Japan. Measured from base to peak, Mauna Kea is the tallest mountain in the world. It is 33,474 feet tall, though only 13,796 feet are above water.

Plateau Mountains
Plateau mountains are also called erosion mountains.
They are created similarly to dome and fold mountains. Two tectonic plates collide into each other causing the land to rise, but not to fold or crack. Over thousands of years, running water then erodes away the land, creating plateau mountains.
The Catskills in New York are an example of plateau mountains.

Interesting Facts
- Mountains can be found on every continent
- The Mid-Ocean Range spans 40,000 miles
- The Andes mountain range is the longest above ground mountain range in the world