One of the most important systems in your body is the immune system. The immune system is a group of cells, tissues, and organs that protect your body from infection and disease. Immune means to be resistant to an infection or substance.
The immune system can tell the difference between healthy, functioning cells found in the body and unhealthy cells. Unhealthy cells could be damaged cells or infectious microbes like viruses and bacteria.
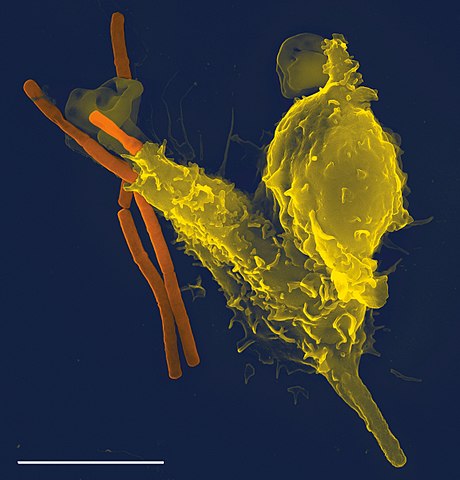
The Immune Response
The immune system responds to antigens and other unhealthy cells in the body with a process called the immune response. Things like diseases and viruses are called antigens.
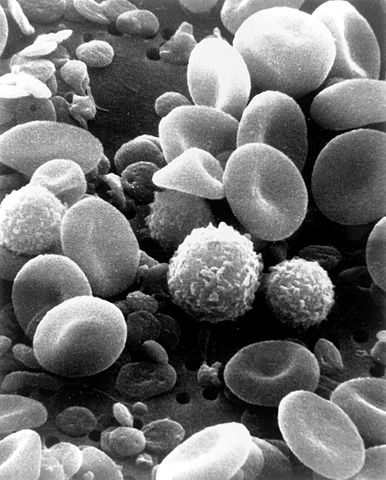
White blood cells, also called leukocytes, are important cells that hunt unhealthy organisms in your body. White blood cells are created in your spleen, thymus, and bone marrow. They are also stored in special glands in your body called lymph glands.
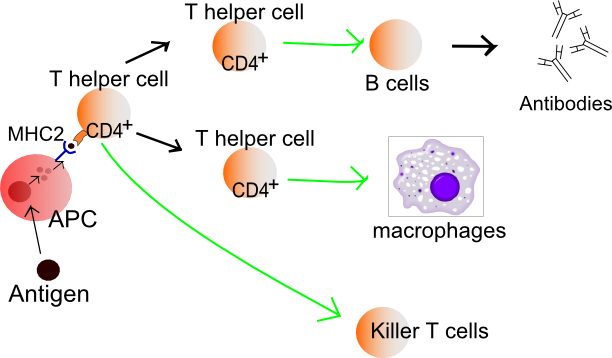
There are two types of leukocytes: phagocytes and lymphocytes. Phagocytes attack antigens in your body. Lymphocytes create antibodies and T cells.
Antibodies identify specific antigens and attach onto them. They join up with T cells to destroy these antigens. Antibodies stay in your body and remember the specific antigens. That way if that disease or virus returns, it can be attacked again.
Immunizations prevent disease by introducing a non-dangerous form of antigen to the body. This triggers antibodies that identify the disease and protect the body from later attacks.
Immunity
There are three types of immunity: innate, active, and passive.
Innate immunity is the type of immunity that you are born with. It is the body’s natural defense against antigens. Some examples of innate immunity are your skin and enzymes in your stomach.
Active immunity develops as you age. When antigens enter your body, your white blood cells attack it and remember it. This is your active immune system.
Passive immunity is immunity that comes from another source and only lasts a short time. An example of passive immunity is found in breastmilk.
When a baby is born, it doesn’t have a strong active immune system. Breastmilk from the mother can temporarily improve a baby’s immune system.
Parts of the Immune System
Some of the main parts of the immune system are: skin, bone marrow, bloodstream, lymph nodes, thymus, and spleen.
The skin is the body’s first defense against infection. It is a barrier keeping antigens out of the body and contains specific immune cells.
Bone marrow is where white blood cells are created. It is a yellowish substance found in the middle of different bones. Bone marrow contains stem cells which are immature cells that can develop into many different types of cells, including white blood cells.
The bloodstream is where white blood cells are found. They circulate throughout the body searching for antigens and other unhealthy cells.
Lymph nodes are part of the lymphatic system. They are small glands in the body that store leukocytes. They also contain lymph, a fluid that carries the leukocytes to different parts of the body.
The thymus is a small organ in the upper chest. It creates T cells.
The spleen is an organ that is located behind the stomach. It contains leukocytes and processes information. When antigens are discovered the spleen sends leukocytes to the bloodstream to deal with them.
Interesting Facts:
- The thymus gets its name from its thyme leaf shape
- The most common type of phagocyte is called neutrophil
- Immune deficiency disorders, autoimmune disorders, allergic disorders, and cancer are the four main disorders of the immune system